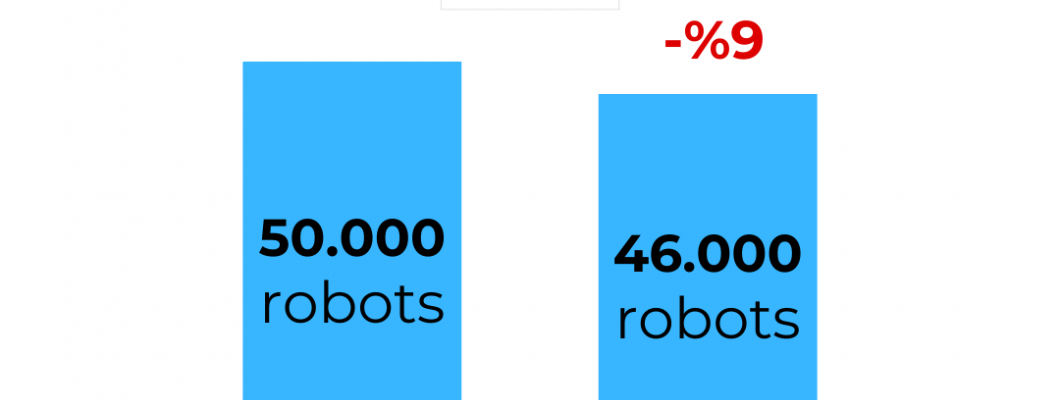
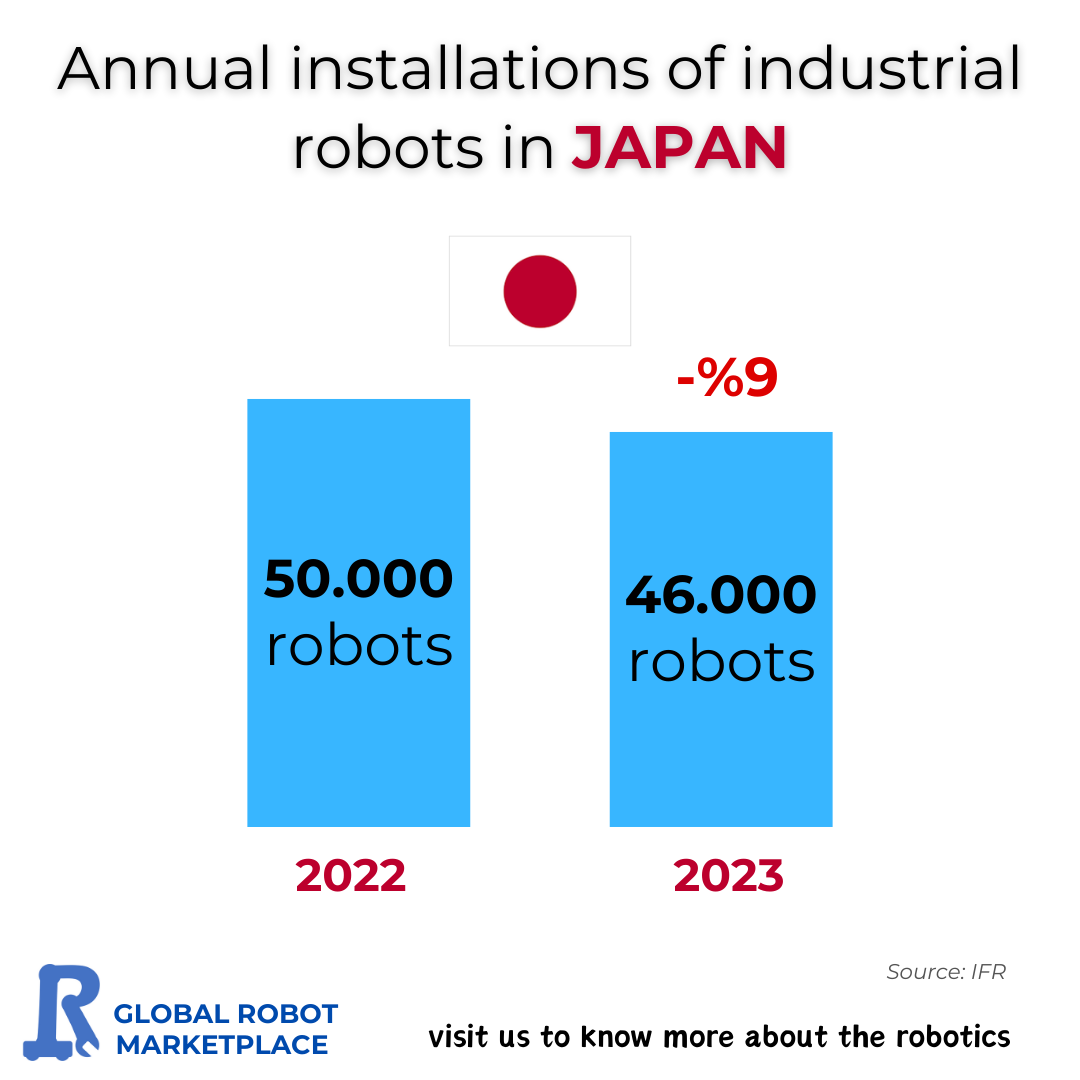
Japan has long been recognized as a global leader in robotics, particularly in the development and deployment of industrial robots. However, as the data presented in the image reveals, 2023 marked a significant downturn in the number of industrial robots installed in the country. With installations dropping from 50,000 units in 2022 to 46,000 units in 2023, 9% decrease, this shift prompts several questions about the current state and future of Japan’s robotics industry.
Understanding the Numbers
The decline in installations, as reported by the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), is notable for several reasons:
- The Scale of Reduction: A 9% drop might not seem drastic at first glance, but in an industry where growth is often steady or exponential, such a reduction could indicate underlying issues.
- Impact on Global Trends: Japan has traditionally been one of the largest markets and producers for industrial robots, so this downturn could ripple through the global robotics ecosystem.
Possible Causes of the Decline
The drop in robot installations in Japan may be attributed to a range of economic, industrial, and geopolitical factors:
Economic Slowdown:
- Japan’s economy has faced challenges, including slow GDP growth and inflationary pressures. Businesses may have delayed or scaled back investments in automation to focus on short-term financial stability.
Labor Market Shifts:
- Despite the declining population and labor shortages, some industries might still rely on human labor due to the initial high costs of integrating robotics into their workflows.
Supply Chain Disruptions:
- The global semiconductor shortage, compounded by disruptions in the supply chain, could have hindered the production and distribution of industrial robots.
Market Saturation:
- In some sectors, Japanese companies might already have high levels of automation, leading to fewer opportunities for new installations.
Policy and Regulation:
- Delays in government initiatives to promote robotics or restrictive trade policies could also play a role in this trend.
Implications for the Industry
The decrease in robot installations has both immediate and long-term implications for Japan and the broader robotics market:
Competitive Pressure:
- Japan faces growing competition from other industrial hubs like China, South Korea, and Germany. A slowdown in installations could jeopardize its leading position in the industry.
Technological Innovation:
- A reduction in installations does not necessarily mean a slowdown in innovation. Japanese robotics companies might be focusing on research and development, aiming to introduce next-generation robots with advanced capabilities.
Workforce Dynamics:
- With fewer robots being installed, industries may face challenges in maintaining productivity amid a shrinking workforce. This might push companies to adopt hybrid models of automation and human labor.
Global Perceptions:
- As one of the pioneers in robotics, Japan’s declining installations could influence perceptions about the maturity and growth potential of the global robotics sector.
Opportunities Amidst Challenges
Despite the decline, the industrial robotics market in Japan has several opportunities for recovery and growth:
Diversification:
- Japanese robotics companies could explore applications beyond traditional manufacturing, such as healthcare, logistics, and agriculture.
Artificial Intelligence Integration:
- Combining robotics with AI could drive demand for robots capable of complex, adaptive tasks.
Global Expansion:
- Companies might focus on exporting robots to regions with burgeoning industrial automation needs, such as Southeast Asia and Africa.
Sustainability Goals:
- The push for green manufacturing and energy efficiency could spur investments in robots designed to optimize resource usage.
Conclusion
The 9% decline in industrial robot installations in Japan serves as both a wake-up call and an opportunity for introspection. While the challenges are clear, Japan’s legacy in robotics, combined with its capacity for innovation, suggests that this downturn could be temporary. By addressing economic and market dynamics, embracing new technologies, and expanding into emerging industries, Japan’s robotics sector can reaffirm its leadership in the global arena.
As we move forward, understanding the factors behind these shifts will be crucial for stakeholders across industries. For a nation that has often set the pace for technological advancement, the next steps taken by Japan will undoubtedly shape the future of robotics worldwide.
