
The robotics industry has undergone remarkable growth over the past decade, with significant advancements in both traditional industrial robots and a newer class of robots called collaborative robots, or "cobots." This article dives into the key differences, market trends, and the growing role of cobots in the robotics landscape.
Understanding Cobots and Industrial Robots
Industrial Robots are the traditional robots used in manufacturing and heavy industries. They are typically programmed to perform repetitive tasks with high precision and speed, such as welding, painting, and assembly. These robots often operate in isolated environments due to safety concerns, as they can pose risks to human workers due to their size, speed, and power.
Cobots or "collaborative robots," on the other hand, are designed to work alongside human workers, augmenting their capabilities. Cobots are generally smaller, easier to program, and equipped with safety features that enable them to operate safely in close proximity to people. They are increasingly used in applications such as packaging, quality inspection, and light assembly tasks.
Market Share: Cobots vs. Industrial Robots
According to data from the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), industrial robots currently hold a dominant 90% share of the robotics market, while cobots account for around 10%. This imbalance reflects the long-standing presence and scale of traditional industrial robots in sectors like automotive, electronics, and heavy manufacturing, where automated, high-speed production lines are crucial.
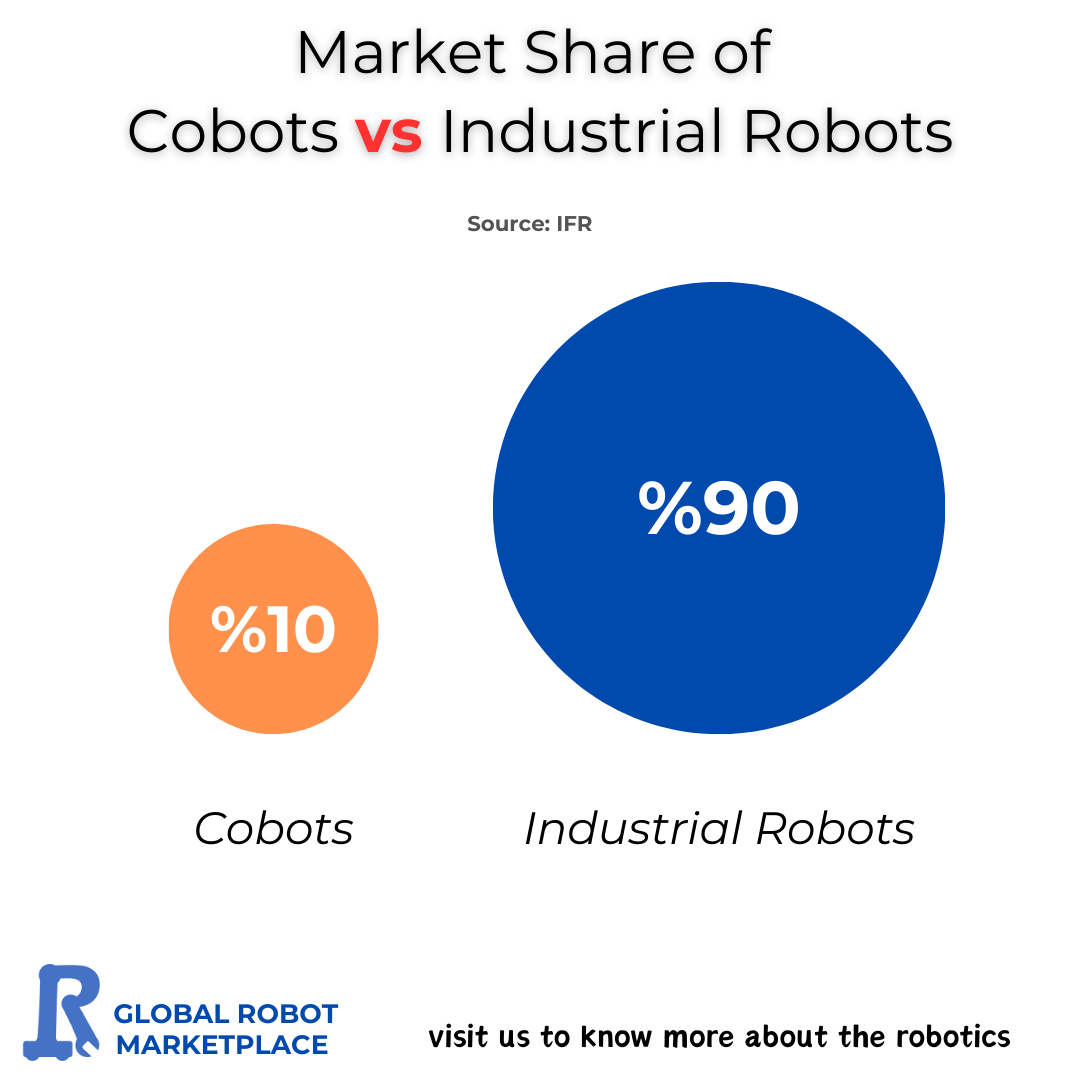
However, the 10% share held by cobots represents significant growth, given that they were a relatively niche category until recently. Their rise can be attributed to their flexibility, ease of deployment, and the growing demand for automation in small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Factors Driving Cobot Adoption
Flexibility and Ease of Use: Unlike industrial robots, which often require complex programming and significant setup time, cobots are designed to be more user-friendly. They can be reprogrammed and deployed across different tasks, making them ideal for manufacturers with varying production needs.
Human-Robot Collaboration: Cobots are built to work in shared spaces with human employees, offering safer interactions and reducing the need for physical barriers. This is particularly valuable in settings where human workers can perform high-skill tasks while cobots handle repetitive or strenuous parts of the process.
Growing Demand from SMEs: Large industrial robots are often costly and require a substantial investment in infrastructure, making them impractical for many smaller companies. Cobots, with their lower upfront costs and versatility, provide an accessible entry point for automation, especially for SMEs looking to increase productivity without a large capital outlay.
Rising Labor Costs and Shortages: In many regions, labor shortages and rising wages are prompting businesses to consider automation as a solution. Cobots provide a way to augment labor capabilities, allowing human workers to focus on more complex tasks while robots handle simpler, repetitive jobs.
Challenges and Limitations of Cobots
While cobots offer numerous advantages, they do face certain limitations compared to traditional industrial robots:
Lower Speed and Payload Capacity: Cobots generally have lower speed and payload capacities than industrial robots, which limits their effectiveness in heavy-duty applications.
Higher Initial Costs: Although cobots can be more cost-effective in the long run, their upfront costs are still significant, which can be a barrier for smaller businesses.
Limited Awareness and Skill Gaps: Many companies, particularly smaller ones, may lack awareness of the potential benefits of cobots or the technical skills needed to integrate them effectively into their processes.
Future Outlook: Will Cobots Gain More Market Share?
The global market for cobots is expected to grow substantially as more companies recognize their advantages and as cobot technology continues to improve. Some experts forecast that cobots will account for a much larger share of the market over the next decade, driven by advancements in AI, machine vision, and sensor technology. As cobots become more capable and affordable, their adoption across various industries, including logistics, healthcare, and consumer goods, is likely to increase.
Conclusion
The 90%-10% market share between industrial robots and cobots illustrates both the established dominance of traditional robotics and the exciting potential of collaborative robots. Cobots are rapidly becoming an essential tool in modern manufacturing, especially for companies seeking flexibility, safety, and cost-effective automation. As the robotics landscape continues to evolve, cobots are well-positioned to capture an increasing share of the market, reshaping the future of industrial automation.
For businesses exploring automation solutions, understanding the benefits and limitations of both types of robots is crucial in making the right investment decisions. To learn more about the world of robotics and the latest developments, visit the Global Robot Marketplace for insights, products, and resources.
