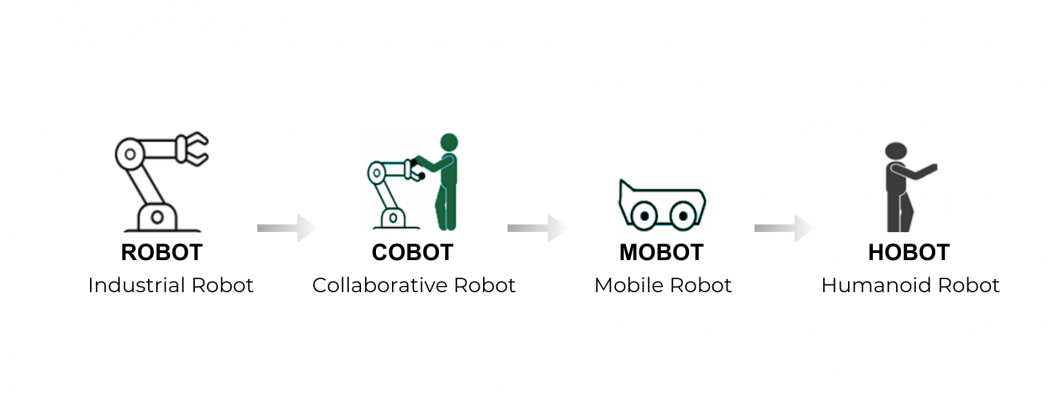
The field of robotics has evolved tremendously over the last five decades, transforming from simple industrial machines to intelligent humanoid robots. This evolution has been driven by advances in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, automation, and sensor technology. The image illustrates the key phases of robotic evolution, showcasing the progression from traditional industrial robots to modern humanoid robots.

Industrial Robot (ROBOT)
The journey of robotics began with industrial robots, which were introduced in the mid-20th century. These robots were primarily designed to automate repetitive tasks in manufacturing and assembly lines.
- Example: The first industrial robot, Unimate, was deployed in a General Motors plant in the 1960s.
- Functionality: Industrial robots are typically programmed to perform precise, high-speed, and repetitive tasks such as welding, painting, and material handling.
- Limitation: These robots operate in isolated environments due to safety concerns, as they do not interact with humans.
Collaborative Robot (COBOT)
With the demand for safer and more flexible automation, collaborative robots (cobots) emerged. Unlike traditional robots, cobots work alongside human operators, assisting in tasks that require precision, dexterity, and safety.
- Example: Universal Robots' UR series is a leading example of cobots used in various industries.
- Functionality: Cobots are equipped with advanced sensors and AI, allowing them to interact safely with humans without protective barriers.
- Impact: They have revolutionized industries such as healthcare, electronics, and small-scale manufacturing by enabling human-robot collaboration.
Mobile Robot (MOBOT)
The introduction of mobile robots (mobots) marked a significant shift towards autonomous and flexible robotic systems. These robots are capable of navigating dynamic environments using AI-powered mapping and localization techniques.
- Example: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are widely used in warehouses, logistics, and healthcare.
- Functionality: Mobots can transport goods, assist in surveillance, and support various applications in industrial automation and smart cities.
- Advancement: With the integration of AI and the Internet of Things (IoT), mobile robots have become smarter, making autonomous navigation and decision-making possible.
Humanoid Robot (HOBOT)
The latest stage in robotic evolution is the development of humanoid robots (hobots), designed to mimic human behavior, gestures, and even emotions. These robots are built with AI-driven capabilities that enable them to perform complex tasks in service, healthcare, education, and entertainment.
- Example: Boston Dynamics’ Atlas and Tesla’s Optimus are some of the most advanced humanoid robots.
- Functionality: Humanoid robots are equipped with facial recognition, speech processing, and deep learning capabilities to interact naturally with humans.
- Future Prospects: In the coming years, humanoid robots are expected to play a crucial role in caregiving, customer service, and household assistance, making them an integral part of our daily lives.
Conclusion
The evolution of robotics from industrial machines to humanoid robots highlights the rapid technological advancements shaping the future of automation. As AI, robotics, and machine learning continue to progress, robots will become more integrated into our society, enhancing efficiency, safety, and productivity across various industries. The journey of robotics is far from over, and we can expect even more sophisticated and intelligent robotic systems in the near future.
