The world of industrial automation continues to evolve rapidly, with industries increasingly turning to robotics to enhance productivity, efficiency, and precision in their operations. Industrial robots, which are designed to perform tasks with high accuracy and consistency, have become integral to manufacturing processes across various sectors. In 2023, three industries stood out in terms of robot installations: automotive, electronics, and machinery. These sectors lead the global shift toward automation, with each playing a pivotal role in the overall adoption of robotics. This article will explore the factors driving the high rate of robot installations in these top industries and examine the implications for the future of automation.
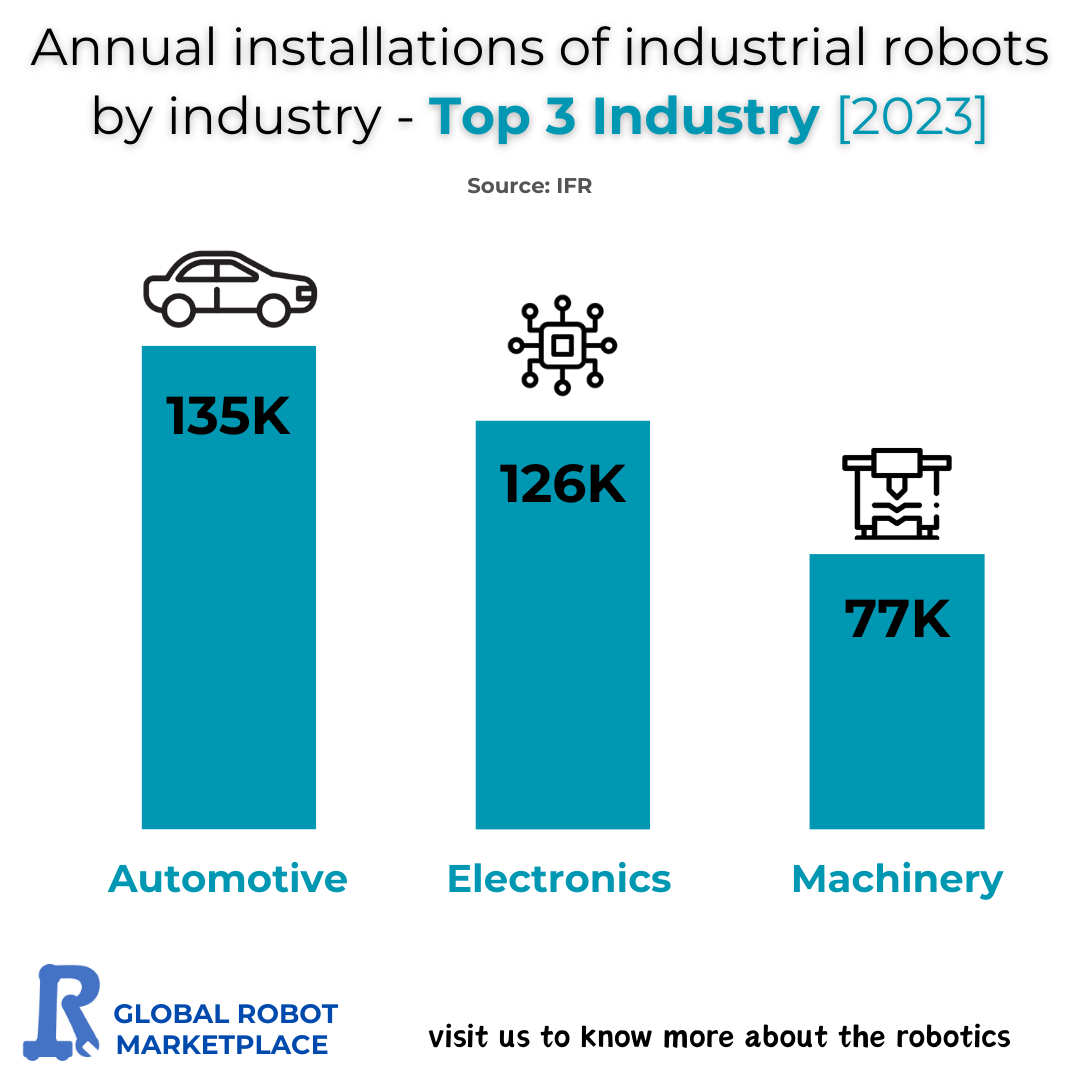
1. Automotive Industry: 135,000 Installations
The automotive industry continues to dominate the landscape of industrial robot installations. In 2023, it saw 135,000 robots installed globally. The reliance on automation in this sector is not a new phenomenon, as car manufacturers have long used robots for tasks such as welding, painting, and assembling components. However, what sets 2023 apart is the growing demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and the significant advancements in autonomous driving technologies, which have added new layers of complexity to the manufacturing process.
a. Electric Vehicle (EV) Production
With the global push toward greener transportation solutions, the automotive industry is undergoing a seismic shift in production. The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) has necessitated a more automated approach to manufacturing due to the complexity of battery production, as well as the need for lightweight, durable materials in EV assembly. Robots are critical in assembling the sophisticated battery modules used in EVs, as well as in precision tasks like motor assembly and electronics integration. This increased demand for automation in EV production is a key driver behind the high robot installation numbers in the automotive sector.
b. Flexible and Modular Manufacturing
In response to the demand for more customized vehicle models, car manufacturers are moving toward more flexible, modular production lines. Robots, especially collaborative robots (cobots) that can work alongside human operators, allow factories to quickly adapt to changing production needs. This flexibility is essential in an era where consumer preferences are constantly shifting, and companies need to adjust production lines for different vehicle models, including hybrids, EVs, and traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. The ability to reprogram robots for different tasks without significant downtime has made automation indispensable in modern car manufacturing.
2. Electronics Industry: 126,000 Installations
The electronics industry comes in a close second, with 126,000 robots installed in 2023. The need for high precision and the ability to handle tiny, delicate components are driving automation in this sector. With the continuous demand for smaller, faster, and more powerful devices, manufacturers of electronics—especially semiconductors, consumer electronics, and high-tech devices—are increasingly turning to robotics to maintain quality and scale production.
a. Semiconductor Manufacturing
Semiconductors are the backbone of modern electronics, and their production requires extreme precision and clean environments. Any contamination or error in the manufacturing process can lead to costly defects. Robots, which are capable of working in highly controlled environments without the risk of introducing human error, have become critical in semiconductor fabrication. They are used for wafer handling, inspection, and even packaging, ensuring that each step of the production process is carried out with the utmost precision.
b. Consumer Electronics
The consumer electronics sector is one of the most rapidly evolving industries, driven by constant technological advancements and high consumer demand for new products. Manufacturers face intense pressure to produce devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, and wearables on a massive scale while maintaining strict quality standards. Robots excel in handling delicate materials, performing micro-assembly, and ensuring that the tiny components inside electronics are placed with extreme accuracy. As the electronics industry continues to push the boundaries of miniaturization, the role of robots in production becomes increasingly essential.
c. Supply Chain Automation
In addition to manufacturing, the electronics industry is also leveraging robots for warehouse and supply chain automation. The rise of e-commerce and the need for efficient distribution of electronic goods have led to an increased adoption of automated solutions in logistics. Robots are used for tasks such as sorting, packing, and inventory management, which helps companies optimize their supply chains and reduce costs.
3. Machinery Industry: 77,000 Installations
Rounding out the top three industries, the machinery sector saw 77,000 robot installations in 2023. While this industry has traditionally relied on manual labor for many tasks, the growing demand for greater precision, efficiency, and safety is pushing machinery manufacturers to adopt more robotic solutions.
a. Heavy Machinery Assembly
In the machinery industry, robots are used for assembling large, heavy, and often complex equipment. These tasks are not only physically demanding but also require a high degree of accuracy to ensure the machinery functions correctly. Robots are capable of performing tasks such as welding, fastening, and material handling with consistency and precision, which reduces errors and improves overall production quality. The ability to handle heavy loads and work in environments that may be dangerous or uncomfortable for humans also makes robots an ideal solution for many machinery manufacturers.
b. Precision Machining
Robots are also widely used in precision machining processes, where accuracy is critical. This includes tasks like cutting, grinding, and polishing parts to exact specifications. In sectors such as aerospace, where the machinery must meet strict quality standards, robotic automation ensures that each component is manufactured with the highest level of precision. This not only improves the quality of the final product but also reduces waste and lowers production costs.
c. Improving Worker Safety
Another key driver of robot adoption in the machinery sector is the need to improve worker safety. Many tasks in machinery production involve working with heavy materials, sharp tools, or hazardous environments. By automating these tasks, companies can reduce the risk of workplace accidents and ensure that their employees are working in safer conditions. Robots can handle the repetitive, dangerous, or strenuous jobs, allowing human workers to focus on higher-value tasks such as programming and maintenance.
The Growing Role of Robotics Across Industries
The automotive, electronics, and machinery sectors are leading the charge in the adoption of industrial robots, but they are by no means the only industries embracing automation. Other sectors, such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and logistics, are also seeing significant growth in robot installations. The versatility and adaptability of modern robots make them an attractive solution for a wide range of applications.
a. Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
One of the most significant trends in industrial automation is the rise of collaborative robots, or cobots, which are designed to work alongside human operators. Unlike traditional industrial robots, which are often confined to safety cages, cobots are equipped with advanced sensors and software that allow them to safely interact with humans. This opens up new possibilities for automation in smaller facilities or in tasks that require a combination of human skill and robotic precision.
b. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Another factor driving the growth of robotics is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies enable robots to learn from their environments and improve their performance over time. For example, AI-powered robots can optimize production processes, predict maintenance needs, and even make real-time adjustments to improve efficiency. This level of intelligence is transforming robots from simple, task-specific machines into adaptable, self-learning systems that can handle increasingly complex tasks.
c. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
As industries across the globe strive to reduce their carbon footprint and meet environmental goals, robotics offers a way to improve sustainability in manufacturing. Robots are often more energy-efficient than traditional machinery, and they can optimize processes to minimize waste. In sectors such as automotive and electronics, where sustainability is becoming a key competitive differentiator, the ability to reduce energy consumption and streamline production through automation is a major advantage.
Conclusion
The automotive, electronics, and machinery industries are leading the global shift toward industrial automation, each with its own set of challenges and opportunities driving the adoption of robotics. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even greater levels of automation across these and other sectors. The rise of collaborative robots, AI, and sustainable practices will further enhance the capabilities of industrial robots, making them an indispensable part of modern manufacturing.
For businesses looking to stay competitive in an increasingly automated world, investing in robotic solutions is no longer an option—it’s a necessity. The future of manufacturing is automated, and those who embrace this trend will be best positioned to succeed in the years to come.
Global Robot Marketplace
